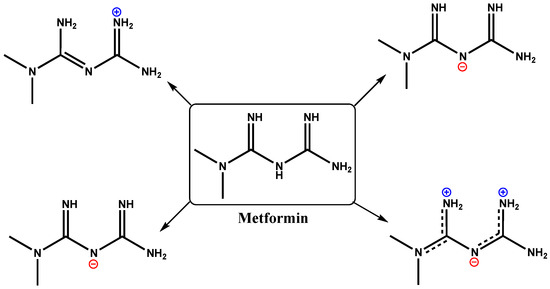
Title: Synthesis, Characterization and Structural Analysis of Two New Biguanide Complexes
Abstract:
Utilizando a expertise acumulada ao longo de muitos anos, o LaMuCrEs possui múltiplos interesses e linhas de pesquisa, como Mineralogia, Insumos farmacêuticos e Compostos de Coordenação.

Abstract:
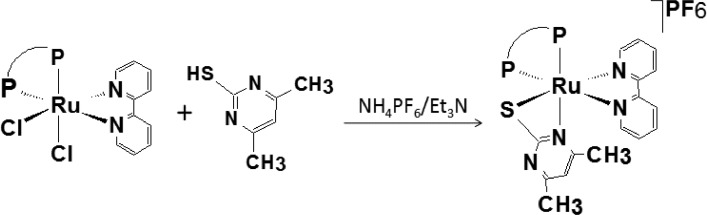
Abstract: Reactions of cis-[RuCl2(P-P)(bipy)] precursors with the SpymMe2 ligand (4,6-dimethyl-2-pyrimidinethiol) yielded complexes of the [Ru(SpymMe2)(P-P)(bipy)]PF6 type, where P-P = 1,2-bis(diphenylphosphino)ethane (dppe - for complex 1), 1,3-bis(diphenylphosphino)propane (dppp - for complex 2) and 1,1’-bis(diphenylphosphino)ferrocene (dppf - for complex 3) and bipy = 2,2’-bipyridine. The new compounds were obtained by displacing the chlorido ligands from the precursors and coordination of one monoanionic 4,6-dimethyl-2-pyrimidinethiol ligand. All complexes were characterized by spectroscopic, electrochemical and elemental analysis techniques, as well as single-crystal X-ray diffraction, where the structures of complexes 1, 2 and 3 showed that the SpymMe2 ligand coordinates to the ruthenium(II) center as bidentated, yielding complexes with the sulfur atom trans positioned to the nitrogen atom from the bipy ligand. A theoretical study of the structures of the complexes was performed using the DFT/B3LYP method. Distances and angles of optimized structures agree with X-ray experimental data. Furthermore, the calculated IR and UV-Vis spectra are compatible with experimental data. Charge decomposition analysis (CDA) and NBO (natural bond orbitals) charges showed that there was an overall charge transfer from bipy and P-P ligands to the ruthenium centers. Higher electrochemical stability and 1H and 31P{1H} NMR shifts of 1, 2 and 3 compared with precursors could be explained by the lower values of calculated molecular orbital energies, NBO charge on atoms and CDA data. Finally, the structure of the isomers of complexes 1, 2 and 3, considering the sulfur atom trans positioned to the phosphorus atom, were optimized, showing that they are slightly less stable, presenting total energy higher, 10.4, 31.5 and 60.5 kJ/mol than 1, 2 and 3, where nitrogen is trans to the phosphorus atom.
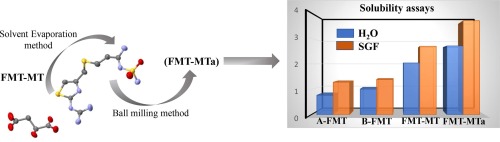
Abstract: Famotidine (FMT) is an orally administered histamine H2-receptor blocker with limited bioavailability since it exhibits low solubility and low permeability. In addition, the recent withdrawal of ranitidine from the market, makes famotidine an interesting candidate to obtain solid forms with improved pharmacokinetic performance. In this work, crystal engineering concepts and the co-amorphous formation strategy were applied to obtain two novel solids. Crystalline famotidine malate (FMT-MT) and a vitreous phase (FMT-MTa) were prepared by solvent evaporation and mechanochemical synthesis, respectively. FMT-MT (monoclinic, S.G. P21/n) crystallizes with one FMT and one co-former molecules in the asymmetric unit forming a (R 228) structural motif. FMT-MT resulted in a salt by proton transfer from one malic carboxylic group to the guanidine moiety of FMT. The three-dimensional packing is described as undulating layers of alternated FMT+ and MT- running along the a direction. FMT-MTa shows the inherent features of amorphous phases according to powder X-ray diffraction and DSC analysis. The higher physical stability was found for amorphous samples maintained at 4 °C up to 60 days. The solubility assays in water, indicate that FMT-MT and FMT-MTa are 2.02 and 2.68-fold more soluble than the marketed polymorph, whereas similar values were obtained in simulated gastric fluid.
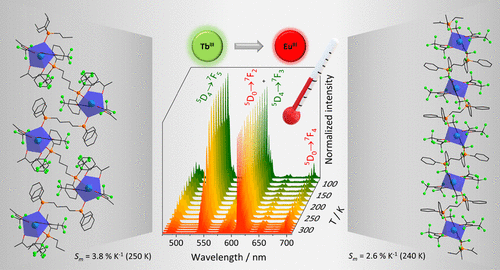
Abstract: TbIII and EuIII systems have been investigated as ratiometric luminescent temperature probes in luminescent coordination polymers due to TbIII → EuIII energy transfer (ET). To help understand how ion-ion separation, chain conformation as well as excitation channel impact their thermometric properties, herein, [Eu(tfaa)3(μ-L)Tb(tfaa)3]n one-dimensional (1D) coordination polymers (tfaa- = trifluoroacetylacetonate, and L = [(diphenylphosphoryl)R](diphenyl)phosphine oxide, R = ethyl - dppeo - or butyl - dppbo) were synthesized. The short μ-dppeo bridge ligand leads to a more linear 1D polymeric chain, while the longer μ-dppbo bridge leads to tighter packed chains. As the temperature rises from 80 K, upon direct TbIII excitation at 488 nm, the TbIII emission intensity decreases, while the EuIII emission intensity increases after 160 and 200 K when L = dppeo or dppbo, respectively. The temperature-dependent emission intensities, due to TbIII → EuIII ET, enable the development of ratiometric luminescent temperature probes featuring maximum relative thermal sensitivity up to 3.8% K-1 (250 K, L = dppbo, excitation at 488 nm). On the other hand, the same system displays maximum thermal sensitivity up to 3.5% K-1 (323 K) upon ligand excitation at 300 nm. Thus, by changing the excitation channel and bridge ligand that leads to modification of the polymer conformations, the maximum relative thermal sensitivity can be tuned.
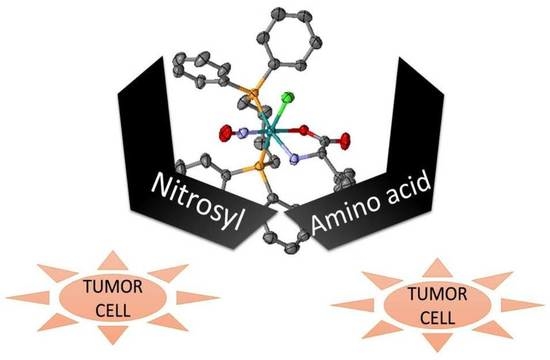
Abstract:
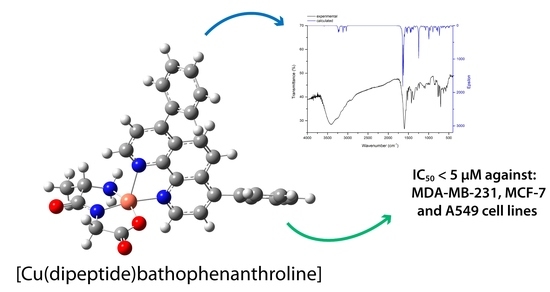
Abstract:
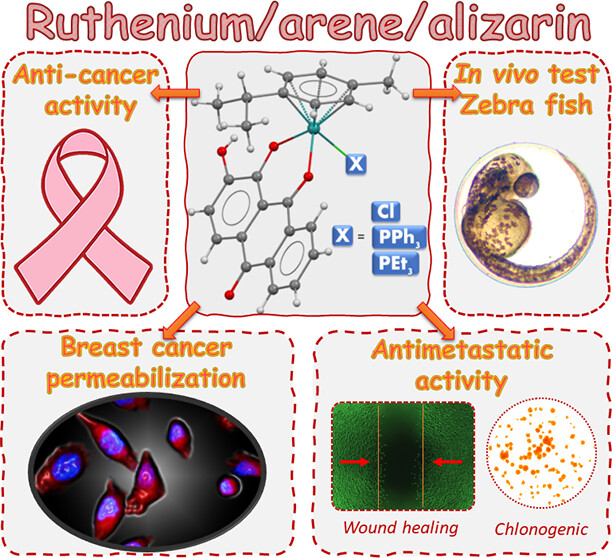
Abstract: Upon exploration of the chemistry of the combination of ruthenium/arene with anthraquinone alizarin (L), three new complexes with the general formulas [Ru(L)Cl(η6-p-cymene)] (C1), [Ru(L)(η6-p-cymene)(PPh3)]PF6 (C2), and [Ru(L)(η6-p-cymene)(PEt3)]PF6 (C3) were synthesized and characterized using spectroscopic techniques (mass, IR, and 1D and 2D NMR), molar conductivity, elemental analysis, and X-ray diffraction. Complex C1 exhibited fluorescence, such as free alizarin, while in C2 and C3, the emission was probably quenched by monophosphines and the crystallographic data showed that hydrophobic interactions are predominant in intermolecular contacts. The cytotoxicity of the complexes was evaluated in the MDA-MB-231 (triple-negative breast cancer), MCF-7 (breast cancer), and A549 (lung) tumor cell lines and MCF-10A (breast) and MRC-5 (lung) nontumor cell lines. Complexes C1 and C2 were more selective to the breast tumor cell lines, and C2 was the most cytotoxic (IC50 = 6.5 μM for MDA-MB-231). In addition, compound C1 performs a covalent interaction with DNA, while C2 and C3 present only weak interactions; however, internalization studies by flow cytometry and confocal microscopy showed that complex C1 does not accumulate in viable MDA-MB-231 cells and is detected in the cytoplasm only after cell permeabilization. Investigations of the mechanism of action of the complexes indicate that C2 promotes cell cycle arrest in the Sub-G1 phase in MDA-MB-231, inhibits its colony formation, and has a possible antimetastatic action, impeding cell migration in the wound-healing experiment (13% of wound healing in 24 h). The in vivo toxicological experiments with zebrafish indicate that C1 and C3 exhibit the most zebrafish embryo developmental toxicity (inhibition of spontaneous movements and heartbeats), while C2, the most promising anticancer drug in the in vitro preclinical tests, revealed the lowest toxicity in in vivo preclinical screening.
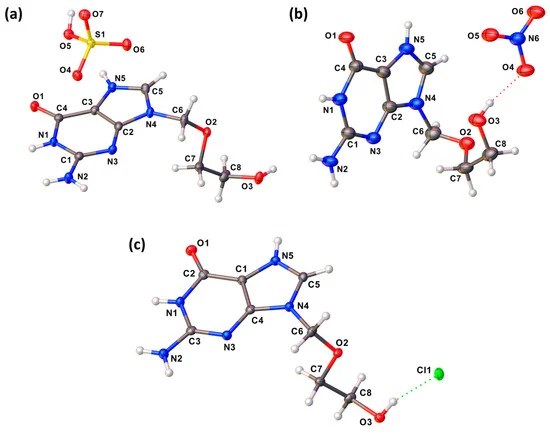
Abstract:
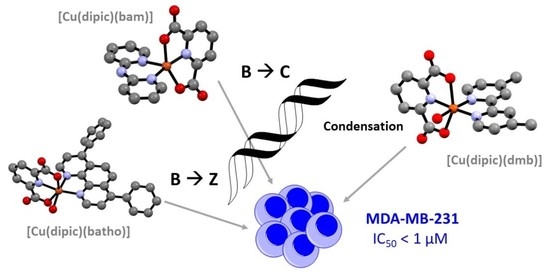
Abstract:
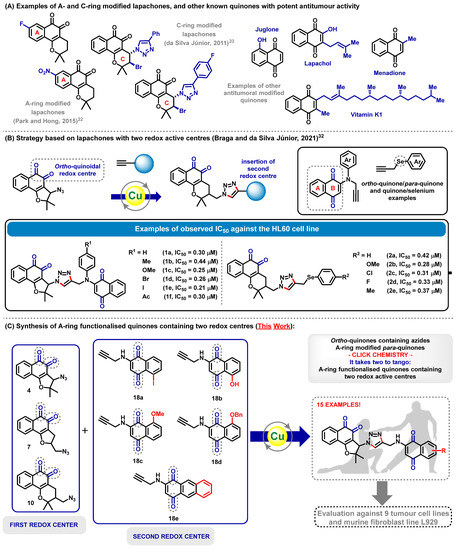
Abstract:

Abstract: The Cerrado biome is the world’s largest and most diversified tropical savanna. Despite its diversity, there remains a paucity of scientific discussion and evidence about the medicinal use of Cerrado plants. One of the greatest challenges is the complexity of secondary metabolites, such as flavonoids, present in those plants and their extraction, purification, and characterization, which involves a wide range of approaches, tools, and techniques. Notwithstanding these difficulties, the search for accurately proven medicinal plants against cancer, a leading cause of death worldwide, has contributed to this growing area of research. This study set out to extract, purify, and characterize 3-O-methylquercetin isolated from the plant Strychnos pseudoquina A.St.-Hil. (Loganiaceae) and to test it for antiproliferative activity and selectivity against different tumor and nontumor human cell lines. A combined-method approach was employed using 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance, thermogravimetric analysis, differential scanning calorimetry, single-crystal X-ray diffraction, Hirshfeld surface analysis, and theoretical calculations to extensively characterize this bioflavonoid. 3-O-methylquercetin melts around 275 °C and crystallizes in a nonplanar conformation with an angle of 18.02° between the pyran ring (C) and the phenyl ring (B), unlike quercetin and luteolin, which are planar. Finally, the in vitro cytotoxicity of 3-O-methylquercetin was compared with data from quercetin, luteolin, and cisplatin, showing that structural differences influenced the antiproliferative activity and the selectivity against different tumor cell lines.

Abstract:

Abstract: In the crystallization and search for higher multicomponent forms of fluconazole (FLZ), a metastable FLZ polymorph (concomitant) that manifests in the same crystallization system and transforms into the stable FLZ form (II) after the lyophilization process was observed. In this report, we demonstrated and showed how this FLZ polymorph 10 (Mw = 306.79 g/mol) of the monoclinic C2 space group was detected and reproduced through a controlled lyophilized experiment, and modeled differentiation between vibrational and absorption modes of FLZ functionalities like C=O, OH, –CH2 and –NH. The FLZ polymorph shows strong O–H···N and weak C−H···X (X = N, and F) hydrogen bond and the presence of pi-pi bond interactions in the overlapping triazole rings. The combination of vibrational spectroscopic techniques (Raman/FT-IR) and principal component analysis (PCA) aid the development of important models for polymorph screening and identification. In addition, X-ray diffraction (powder and single crystal) techniques support the polymorph characterization and structure depiction. The PCA models and X-ray diffraction analyses confirmed the newness of FLZ polymorph 10, and further solid-state characterization using thermal techniques (DSC and TGA) affirmed its uniqueness and novelty. Finally, the thermal stability and solubility studies on the new FLZ polymorph were determined to understand its structure properties and compare these with previously reported polymorphs of FLZ.